What makes the IBM PC so vital within the historical past of non-public computing? Its influence goes far past being a easy product – it is a image of standardization and accessibility that reshaped the trade for many years to return.
Consider this in immediately’s phrases… what differentiates a gaming desktop from a house console? Is it the flexibility to decide on any components and peripherals you need? Or maybe the help for video games created many years earlier than the pc itself? Previously, the primary distinction could be a keyboard.
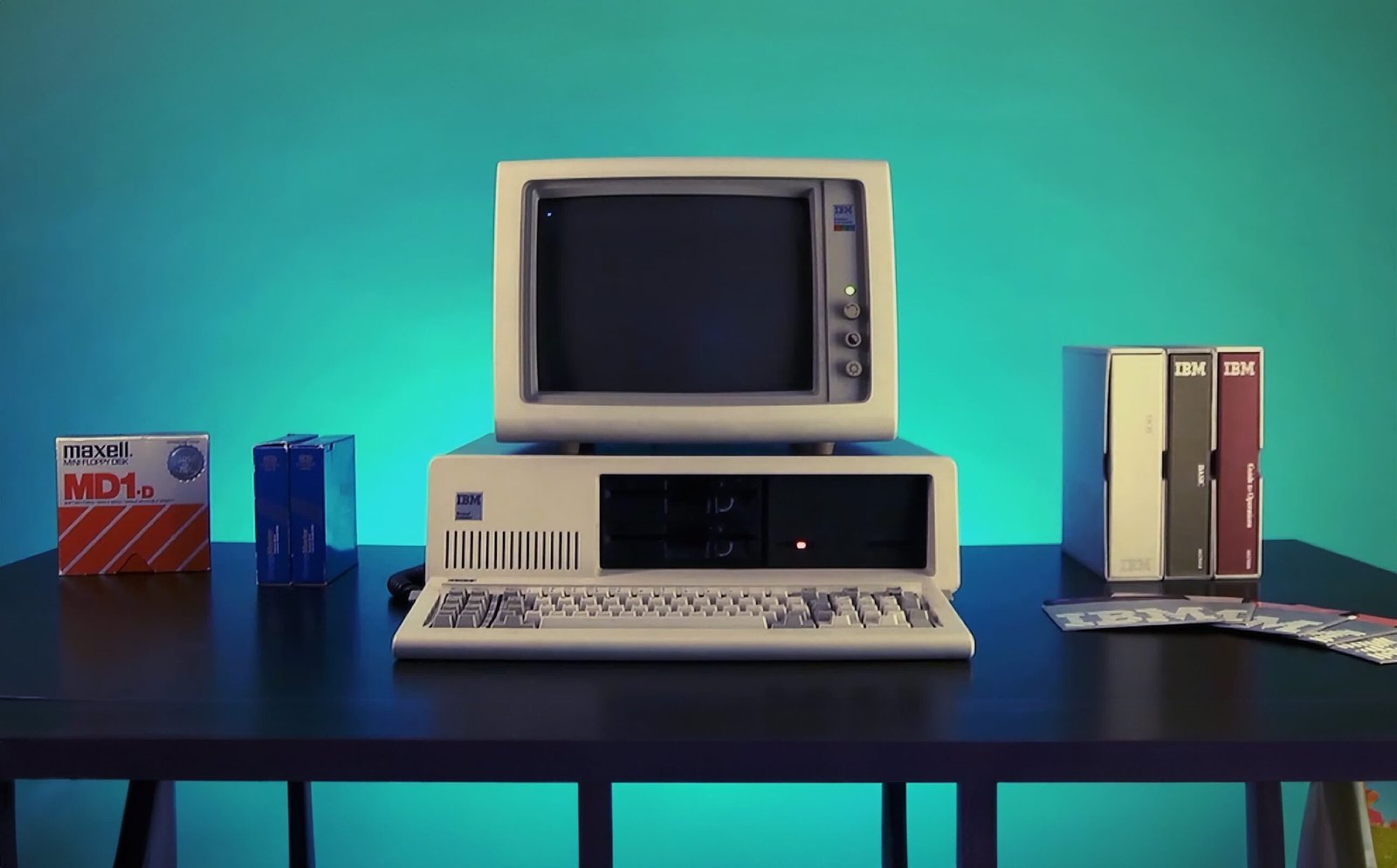
A typical early-Nineteen Eighties laptop. Picture: Miles Bintz
As of late, Apple is the one firm that produces computer systems with unique software program and peripherals. However within the early Nineteen Eighties, it was the norm. Again then, house computer systems have been seen as upgraded consoles, primarily used for gaming and coding. In lots of instances, they have been even made by the identical corporations. The IBM PC strategy modified the very definition of what a private laptop could possibly be.
By embracing third-party {hardware} and software program, the IBM PC standardized the pc market, lending its title to your complete trade and granting the Microsoft and Intel duopoly (later additionally AMD) many years of dominance.
The Artwork of Compromise
Within the Nineteen Seventies, IBM was the most important laptop firm on this planet. Nonetheless, it targeted on creating room-filling mainframe computer systems for governments, universities, and firms, relatively than serving house customers.
That started to alter with the discharge of the spreadsheet app VisiCalc in late 1979. VisiCalc turned house computer systems from fanatic devices into one thing that most individuals may discover helpful. This was the signal for Large Blue to get entangled.
IBM’s greatest impediment was itself. With a inflexible 9-to-5 work tradition and an extreme variety of approval committees, any house laptop it may make would develop into out of date by the point it reached the market. IBM workers famously joked that if the corporate wished to ship an empty field to shops, it will nonetheless take 9 months to take action.
IBM workers famously joked that if the corporate wished to ship an empty field to shops, it will nonetheless take 9 months to take action.
IBM government Invoice Lowe was tasked with figuring out the corporate’s technique for the house market. His preliminary plan was daring: purchase Atari, which had efficiently entered the house computing house with its 8-bit computer systems.
Nonetheless, IBM Chairman Frank Cary rejected the thought, preferring as a substitute to create a small, “unbiased enterprise unit” inside IBM. Lowe got here up with a plan, nicknamed Challenge Chess, to create a house laptop inside a 12 months.
IBM chairman Frank Cary
With such a decent schedule, IBM determined to design solely important parts, such because the case and motherboard, whereas outsourcing all the things else. Philip “Don” Estridge was put in command of the venture, and the pc was codenamed Acorn.
The Beginning of Compatibility
The selection of a CPU for IBM’s first private laptop appeared easy on the time, however in the end formed the way forward for fashionable computing. IBM selected Intel’s 8088 microprocessor over the extra highly effective 16-bit 8086, a call pushed primarily by price, time constraints, and compatibility with present 8-bit {hardware}. Whereas many engineers criticized this selection as a compromise, it turned out to be a pivotal second in expertise historical past.
The 8088 was primarily based on the 16-bit Intel 8086 and used the identical x86 instruction set, nevertheless it featured an 8-bit exterior bus. This design allowed IBM to make the most of cheaper, broadly out there parts, akin to these appropriate with the Intel 8085-based System/23 Datamaster. The choice had large implications: the x86 structure of the 8088 turned the muse for future generations of processors, together with immediately’s CPUs.
Additionally, to keep away from reliance on a single provider, IBM required Intel to license its x86 processors to a different producer, which led to a partnership with AMD.
Intel 8088 made by AMD. Picture: AMD pre-historico
The choice was a tad extra sophisticated when selecting an working system. The pure candidate was CP/M, created by Gary Kildall and used on many house computer systems on the time. Many tales have been informed about an IBM go to gone fallacious, however the true subject was that IBM realized that creating an x86 model of CP/M would have taken Kildall’s firm (Digital Analysis) too lengthy, and would have made the pc too costly. IBM wanted an alternate, quick.
The answer got here from Seattle Pc Merchandise (SCP). Tim Paterson, a programmer from SCP, had developed an x86-compatible working system unofficially known as QDOS (Fast and Soiled Working System). It used CP/M’s publicly out there utility programming interface (API), making it simple for builders to port their functions.
Like most house computer systems on the time, the IBM machine would come with a ROM (read-only reminiscence) chip with a model of Microsoft BASIC, so customers may create their very own apps – the simplest technique to get apps within the early days.
Philips P2000C operating CP/M. Picture credit score: tony_duell
The corporate turned to Microsoft to deal with the OS negotiations. Microsoft struck a take care of SCP to license QDOS, initially paying solely $25,000 in royalties as a result of IBM was their sole consumer. Later, Microsoft employed Paterson to adapt QDOS for IBM’s wants, together with help for the newer 5.25-inch floppy diskettes. Recognizing its potential, Microsoft bought QDOS outright from SCP for $50,000, securing unique rights.
At this level, creating a pc could sound easy. You would possibly surprise: why did not dozens of electronics corporations comply with IBM’s strategy? The important thing distinction lay in a single essential innovation: IBM’s Primary Enter/Output System (BIOS).
The BIOS was saved on a ROM chip and acted as a bridge between {hardware} and software program. It allowed the pc to run an working system that wasn’t particularly written for its {hardware}. This layer of abstraction was a game-changer, enabling software program compatibility throughout machines and laying the groundwork for the way forward for private computing.
Large Blue Sea of Clones
The IBM Private Pc (mannequin 5150) was unveiled at a press convention in August 1981 and rapidly turned often called the IBM PC. The launch was accompanied by a intelligent promoting marketing campaign that includes Charlie Chaplin’s character, the Little Tramp. This signaled IBM’s first main foray into promoting computer systems primarily by retail shops.
Technically, you possibly can get an IBM PC for $1,565 (greater than $5,000 immediately), however in the event you wished to save lots of your work, you’d want to attach it to a cassette recorder. Nonetheless, it got here with the Model F keyboard, nonetheless revered immediately for its mechanical high quality. One other fashionable peripheral was the high-resolution 5151 monochrome monitor, providing a formidable decision of 720 x 350 pixels.
For nearly twice the cash, you possibly can improve to a model of the 5150 with two floppy drives (a built-in arduous disk would not arrive till the 5160 mannequin). CP/M-86 was finally provided in its place working system, however its excessive worth – $200 greater than the rebranded PC DOS – was largely dismissed.
IBM estimated it will promote 250,000 items of the PC, largely to small companies, over 5 years. As a substitute, it offered 750,000 items in two years, with many bought for house use. No one thought so many individuals wished an costly laptop at house. Absolutely it was a great laptop, however maybe extra importantly, it was an IBM laptop.
In 1982, Time Journal named the “Private Pc” as its Man of the Year (later renamed “Machine of the Yr”). This determination marked a cultural turning level, recognizing the PC’s profound affect on society and the financial system.
The Rise of Compatibility
Inside a 12 months of its launch, a whole bunch of functions have been out there for the IBM PC. Seeing the chance, many competing laptop producers adopted x86 processors and the rebranded MS-DOS, hoping to faucet into IBM’s rising ecosystem. Microsoft capitalized on this by licensing its OS on a per-machine foundation, a deal it didn’t supply IBM.
Nonetheless, a major hurdle emerged: some software program bypassed the working system and communicated immediately with IBM’s BIOS. Applications just like the revolutionary Lotus 1-2-3 spreadsheet and Microsoft Flight Simulator would not run correctly on these early clones.
The IBM PC, PC Moveable, and Compaq Moveable II. Picture credit score: Marcin Wichary
The answer arrived in 1983 with the Compaq Portable – a suitcase-sized machine that turned the primary true PC-compatible laptop.
IBM’s determination to make use of off-the-shelf parts meant they might not patent the design of the IBM PC, making it comparatively simple for opponents to reverse-engineer the machine and construct “IBM-compatible” clones. Living proof, Compaq achieved compatibility by reverse-engineering IBM’s BIOS utilizing “clean-room” strategies: programmers who had by no means seen the copyrighted supply code recreated its performance.
In 1984, Phoenix Applied sciences adopted go well with, licensing its reverse-engineered BIOS to different producers. This breakthrough allowed smaller corporations to create quicker, cheaper, and extra revolutionary PC clones, outpacing IBM itself.
IBM tried to distinguish its computer systems from the rising wave of PC clones with its Private System/2 (PS/2) collection, launched in 1987. This collection popularized 3.5-inch floppy diskettes and connectors you might be conversant in, like VGA (Video Graphics Array) and the PS/2 mouse/keyboard connector.
Nonetheless, IBM’s determination to make use of proprietary Micro-Channel Structure (MCA) growth slots in its higher-end fashions alienated customers. MCA was incompatible with present Business Customary Structure (ISA) playing cards, successfully isolating IBM from the broader PC market. Each requirements have been finally changed by PCI, the predecessor to immediately’s PCIe, within the Nineties.
Inside just a few years, clone makers flooded the market, undercutting IBM’s personal gross sales as the corporate had inadvertently created a brand new commonplace (the “IBM-compatible PC”), however in the end misplaced management of the market they pioneered.
Whereas IBM faltered, PC clones operating DOS-compatible Home windows techniques surged forward. By the early Nineties, opponents like Packard Bell, HP, and Dell dominated the market, pushing out different techniques just like the Motorola 68000-based Commodore Amiga and Atari ST. Solely Apple Macintosh remained as a viable different.
The ThinkPad model remains to be utilized by Lenovo. Picture: Jarek Piórkowski
Motorola joined IBM and Apple to type the AIM alliance in 1991, meaning to create a competing platform to “Wintel.” The end result was the PowerPC structure and the processors that powered Apple computer systems between 1994 and 2006. In a while, the structure was additionally used to energy house consoles just like the Nintendo Wii, PlayStation 3 and Xbox 360. Nonetheless, Home windows customers caught with x86.
IBM finally exited the PC enterprise, promoting the division to Lenovo for $1.75 billion in 2005. A 12 months later, even Apple switched to Intel CPUs (a call that was reversed some 15 years later).
A Legacy That Endures
Within the Nineties, AMD turned Intel’s major x86 rival after a courtroom ruling allowed it to promote its personal x86 processors. AMD’s introduction of x86-64 – a 64-bit extension of the x86 structure – cemented its relevance.
Whereas Intel tried to switch x86 with its Itanium structure within the early 2000s, customers most popular AMD’s backward-compatible resolution, finally forcing Intel to undertake it as effectively. To at the present time, this structure powers not solely most desktops but in addition fashionable PlayStation and Xbox gaming consoles.
In the meantime, the Arm structure started dominating handheld units within the early 2000s, together with smartphones, tablets, and Nintendo’s moveable consoles. Apple adopted Arm processors in its desktops and laptops between 2020 and 2022.
To think about a world with out the IBM PC, look no additional than an Apple Mac. It is modern however locked down, with {hardware} you possibly can’t improve and compatibility restricted to apps from current years (Macs can have bother operating macOS apps from as late because the 2010s).
Learn subsequent: How 30 Years of Progress Have Changed PCs
With out the IBM PC, house computer systems might need all adopted this closed, proprietary path – the PC was a historic win for tech fans.